Meadow-chernozem soils: characteristics and conditions of formation, vegetation
Meadow-chernozem soil is common on terraced plains and in lowland areas, which are located in the forest-steppe and steppe zones. It is also found in the undergrowth - in the area of low river terraces. This soil is also present on the deluvial trains. The base rocks are deluvium from Cretaceous marls and loess-like loamy soils. The upper layers of this soil are characterized by a granular structure.
Composition and properties of meadow-chernozem soil
Such soils have unique characteristics. There is a lot of humus in the upper horizons of the soil.As the soil deepens, its volume decreases. Humic acids are considered the main part of the soil. In terms of the amount and accumulation of humus, this type of soil can even surpass chernozems.
The reaction of the soil is close to neutral. At the same time, it is characterized by a rather high cation exchange capacity. For 100 grams of soil, it can reach 45 micromoles. In this case, the volume of magnesium is up to 30-50% of the total amount of exchangeable bases.
The profile of this type of soil is characterized by a uniform distribution of silt. This also applies to sesquioxides. As a rule, the soil is washed from easily soluble s alts. It usually has a heavy composition. These soils have a favorable water-stable structure, high water permeability and excellent water-retaining characteristics.
This type of soil resembles black soil. Its distinctive feature is the close location of groundwater to the surface and gleying of the sub-humus horizon and the top of the parent rock from a depth of 1.2-1.5 meters.
Among the meadow-chernozem soil types, saline varieties are often observed, which is associated with the presence of saline groundwater. Soda salinization is typical for the northern forest-steppe, and sulfate salinity for the southern. In the steppe zone, there is a chloride-sulphate type.
Formation conditions
This type of soil is predominantly common in the forest-steppe. However, sometimes it is observed in the steppe and deciduous-forest zones. The largest massifs are localized in intermountain lowlands located in Transbaikalia. They are also found in the West Siberian Lowland. This type is also found in the Oka-Don lowland.
Such soils are considered semi-hydromorphic substitutes for chernozem. However, their distinctive feature is the formation in conditions of high humidity, which is created due to the temporary accumulation of surface runoff moisture or the insignificant depth of the location of soil and groundwater - in the region of 3-7 meters.
This type of soil develops under the cover of meadow-steppe plants. This zone is characterized by various types of grasses. Also, the soil can be formed under sparse grassy forests, in low relief places, in the area of floodplain terraces. This type of soil is often found on low-drainage plains.
The water regime of this type of land is characterized by reciprocal capillary recharge, which is replaced by deep wetting of the soil profile. This situation is observed during most of the growing season.
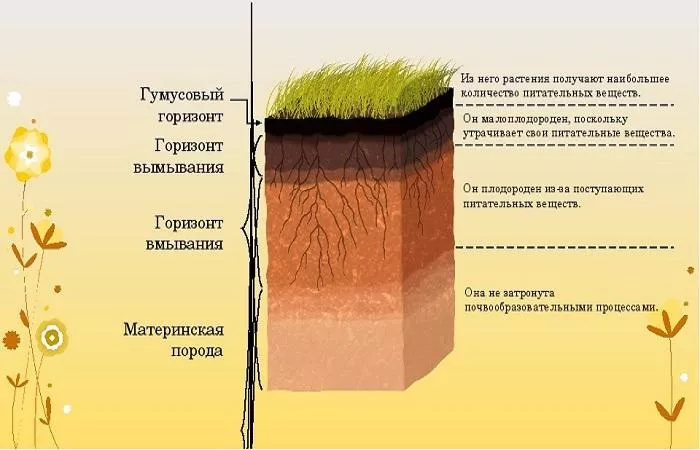
Morphological structure of the profile
The profile of this type of soil is characterized by the following type of morphological structure:
- Humus horizon A - characterized by dark gray color and loose structure. It may be grainy or lumpy-grainy.
- Horizon AB - has a dark gray color with brownish impurities. It is distinguished by a lumpy or coarse-grained structure. The parameters of the total thickness of humus horizons reach 35-70 centimeters. There is effervescence at the bottom.
- Vsa horizon - is located below and is a vaguely expressed illuvial-carbonate horizon. Carbonates are presented in the form of impregnation and in the form of cranes. This structure is typical for the lower part of the profile. In some cases, at a depth of 2-3 meters, small nodules of Fe-Mn are found and symptoms of deep gleying are observed. They are unstable in time and space due to changes in groundwater levels depending on the season and year.
- Sk - is a maternal rock of a pale shade with traces of gleying. It is presented in the form of rusty-buff spots and veins.
Meadow-chernozem soils are characterized by an increased volume of humus compared to the surrounding chernozems. They are considered very fertile. The only exceptions are solonchak and solonetzic genera. In terms of fertility, such soils exceed chernozems.
Main soil-forming processes
Key processes include the following:
- coagulation and biogenic structuring;
- humus-accumulative;
- eluvial-illuvial distribution of carbonates;
- unexpressed gleying.

How to use
This type of soil is considered more fertile than black soil. This is due to better moisture supply. The advantages of such soil are especially evident in dry weather.
In order to rationally use meadow-chernozem soils, it is worth carrying out the same measures as in the case of the use of chernozems. However, it is recommended to irrigate these types of soil very carefully. This is due to the risk of a rapid rise in the groundwater level, which can lead to subsequent salinization and waterlogging.
Since non-saline meadow-chernozem soils are considered the most fertile, they are actively cultivated for arable land. Within the European part of Russia, such soils in their original state can only be found in protected areas.

This type of soil can be used for the cultivation of various types of agricultural vegetation of the corresponding zone. With active use, nitrogen and phosphorus supplements are required. They are recommended to be combined with organic substances.
Meadow-chernozem soils are highly fertile. Therefore, they are actively used in agriculture. To prevent soil depletion, it is important to apply fertilizers in a timely manner.
Recommended
Gray forest soils: characteristics and conditions of formation, fertility and vegetation

Gray forest soils are characterized by certain features. They form in the south of the forest zone and in the forest-steppe, under grassy broad-leaved and small-leaved forests.
Sod-podzolic soils: characteristics and conditions of formation, fertility and vegetation

Characteristics of sod-podzolic soils, how they are formed, composition and structure, humus content. What are the properties of soils, the rules for processing and application, vegetation.
Alluvial soils: characteristics and vegetation of floodplain soils, formation conditions

Under the alluvial types of soil understand the soils of the floodplain part of the rivers. They are often used for growing crops and as pastures for animals.